A “norm” is a statistical description of the assessment results for a defined group. Norms serve as a reference point from which to gauge the results of other individuals completing the same assessment. The “defined group” for The Birkman Method® is adults (ages 17-65) primarily from westernized populations (e.g., North America, UK, western Europe, and Australia) stratified across gender, ethnicity, and occupation.
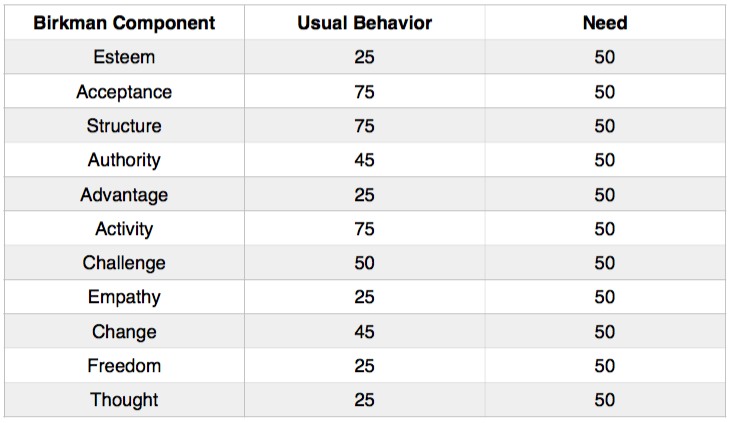
!The population norms for The Birkman Method® are:
You will notice that Stress Behavior is not included in the table above. These results are “directional” rather than absolute. These results do not indicate the degree or intensity of the individual’s stress behavior, but instead the direction their behavior is likely to go when stressed by others or the environment. For example, the individual’s result may indicate they become more direct with others when in stress behavior, but the result does not indicate how direct the person may become.
!Population norms are important for more quickly identifying significant Birkman results for a given component. For example, an individual with a Usual Behavior Structure score of 85 is not extreme relative to the 75 the norm for the scale. Alternatively, a Usual Behavior Structure score of 40 would be more significant, because of the 35 point difference. 2 standard deviations (s), or 20 points on the Birkman continuum, are where the differences become more significant. The further away from the norm, the more significant the difference.